The last spring frost is a significant event for gardeners, as it marks the end of the cold weather and the beginning of the growing season. The date of the last spring frost varies from year to year, depending on the weather conditions. In 2025, the last spring frost is expected to occur on May 15th in the northern United States and April 15th in the southern United States.
After the last spring frost, gardeners can begin planting their warm-season crops, such as tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers. It is important to wait until after the last spring frost to plant these crops, as they are susceptible to damage from cold weather. Gardeners should also be aware of the frost dates for their specific area, as they may vary from the general dates given above.
The last spring frost is a helpful guide for gardeners to determine when to plant their crops. By following the last spring frost dates, gardeners can avoid damaging their plants and ensure a successful growing season.
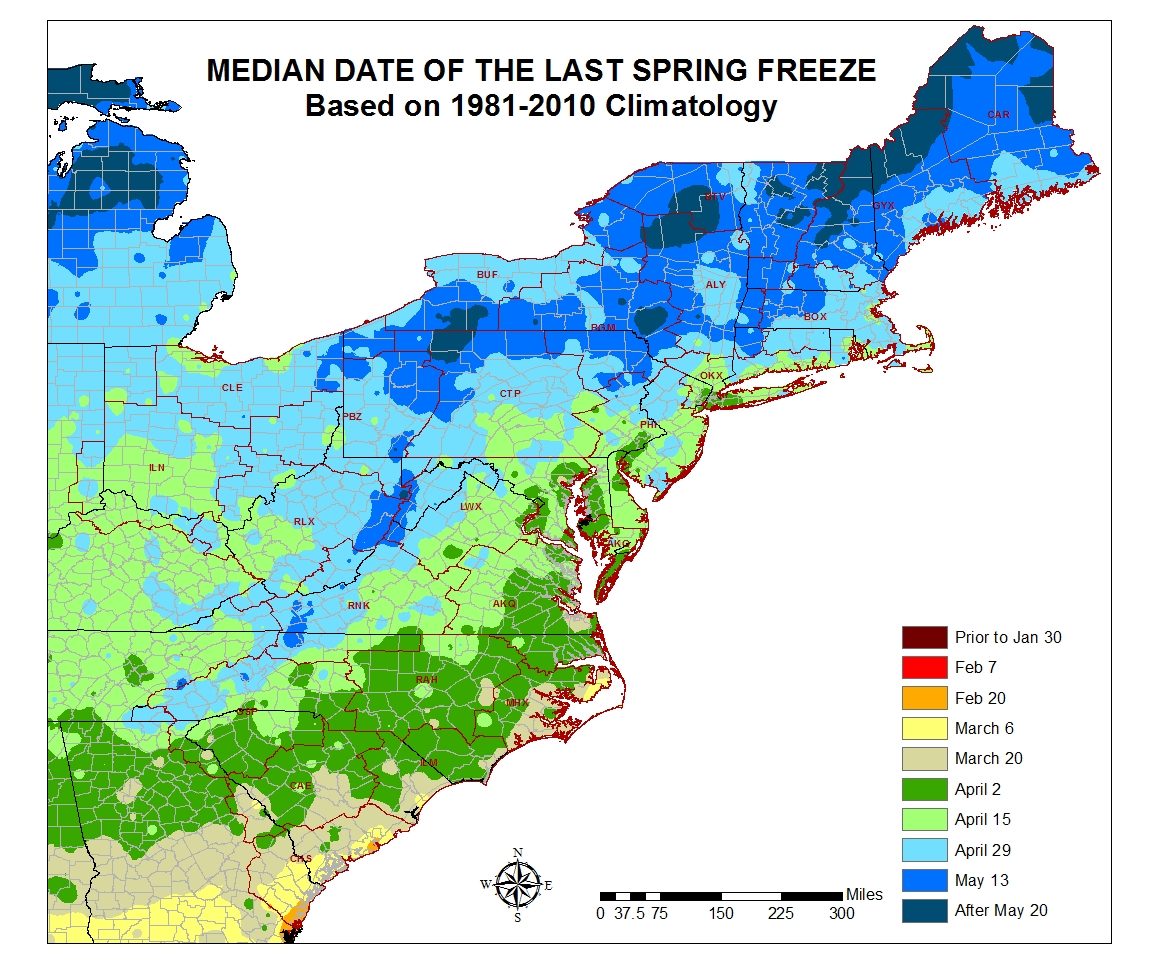
The last spring frost is a significant event for gardeners, as it marks the end of the cold weather and the beginning of the growing season. The date of the last spring frost varies from year to year, depending on the weather conditions. In 2025, the last spring frost is expected to occur on May 15th in the northern United States and April 15th in the southern United States.
/first-and-last-frost-date-2539701-v3-5b102e73fa6bcc0036aae9f4.png)
By following these tips, gardeners can protect their plants from frost damage and ensure a successful growing season.

In the northern United States, the last spring frost is expected to occur on May 15th, 2025. This means that gardeners in this region should wait until after May 15th to plant their warm-season crops, such as tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers. These crops are susceptible to damage from cold weather, so it is important to wait until the danger of frost has passed.
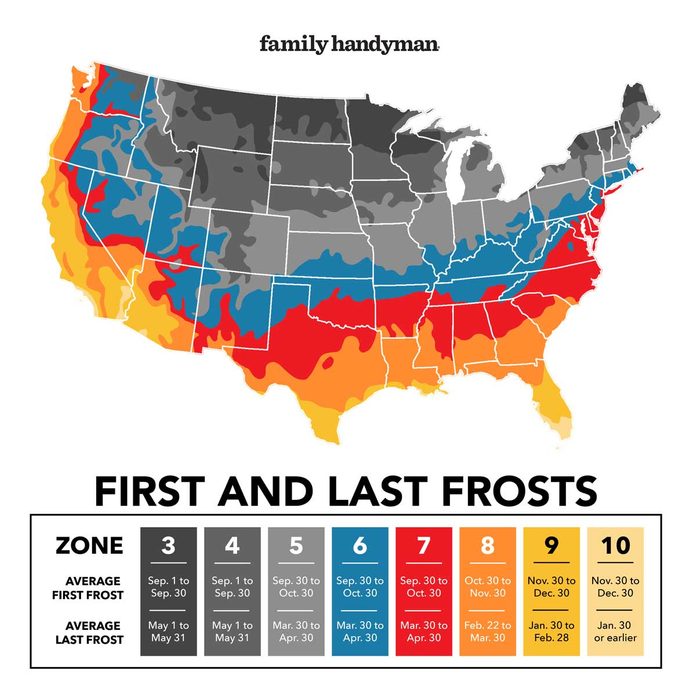
Gardeners should also be aware of the microclimates in their gardens. For example, areas that are sheltered from the wind or that receive more sunlight may warm up earlier than other areas. Gardeners can take advantage of these microclimates by planting their warm-season crops in these areas first.

In addition to planting warm-season crops, gardeners in the northern US can also start to harden off their seedlings in May. Hardening off is the process of gradually exposing seedlings to outdoor conditions. This helps the seedlings to adapt to the colder temperatures and the stronger sunlight. Gardeners can harden off their seedlings by placing them outdoors for a few hours each day, gradually increasing the amount of time they spend outdoors each day.
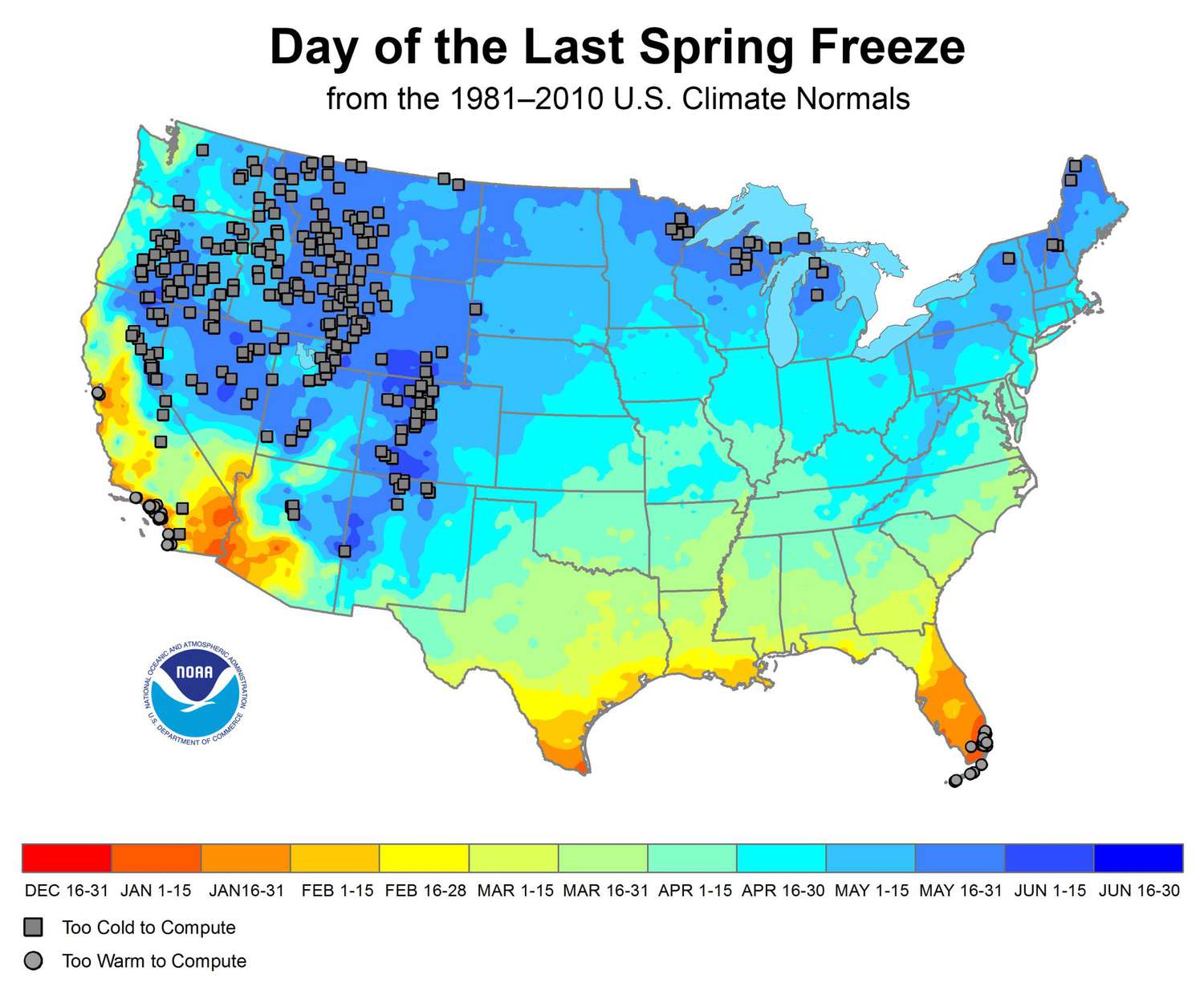
By following these tips, gardeners in the northern US can protect their plants from frost damage and ensure a successful growing season.

It is important to note that the last spring frost date is just an estimate. The actual date of the last frost can vary depending on the weather conditions. Gardeners should monitor the weather forecast and be prepared to protect their plants from frost if necessary.

In the southern United States, the last spring frost is expected to occur on April 15th, 2025. This means that gardeners in this region can start planting their warm-season crops, such as tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers, after this date. These crops are not as susceptible to damage from cold weather as cool-season crops, such as lettuce and spinach, so they can be planted earlier in the spring.
However, it is important to note that the last spring frost date is just an estimate. The actual date of the last frost can vary depending on the weather conditions. Gardeners should monitor the weather forecast and be prepared to protect their plants from frost if necessary.
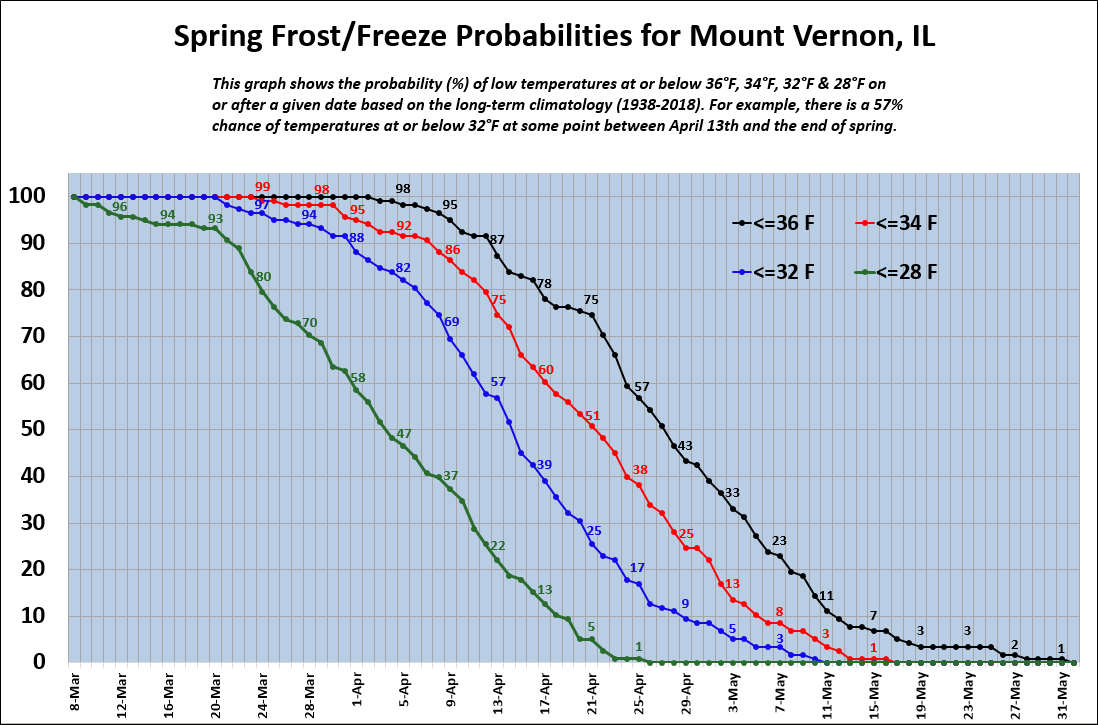
In addition to planting warm-season crops, gardeners in the southern US can also start to harden off their seedlings in April. Hardening off is the process of gradually exposing seedlings to outdoor conditions. This helps the seedlings to adapt to the colder temperatures and the stronger sunlight. Gardeners can harden off their seedlings by placing them outdoors for a few hours each day, gradually increasing the amount of time they spend outdoors each day.
By following these tips, gardeners in the southern US can protect their plants from frost damage and ensure a successful growing season.
Gardeners in the southern US should also be aware of the risk of heat stress. Heat stress can occur when temperatures rise above 90 degrees Fahrenheit. Symptoms of heat stress in plants include wilting, yellowing leaves, and stunted growth. Gardeners can protect their plants from heat stress by providing them with shade, water, and mulch.
Warm-season crops are those that thrive in warm weather and are susceptible to damage from frost. These crops include tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, squash, and melons. In the northern United States, warm-season crops should be planted after the last spring frost, which is typically around May 15th. In the southern United States, warm-season crops can be planted after the last spring frost, which is typically around April 15th.
Tomatoes are one of the most popular warm-season crops. They require full sun and well-drained soil. Tomatoes should be planted 2-3 feet apart and watered regularly.
Peppers are another popular warm-season crop. They come in a variety of shapes and colors. Peppers require full sun and well-drained soil. Peppers should be planted 18-24 inches apart and watered regularly.
Cucumbers are a refreshing and healthy warm-season crop. They can be grown in full sun or partial shade. Cucumbers require well-drained soil and should be planted 12-18 inches apart. Cucumbers need regular watering, especially during hot weather.
Squash is a versatile warm-season crop that can be used in a variety of dishes. Squash requires full sun and well-drained soil. Squash should be planted 3-4 feet apart and watered regularly.
Cold-sensitive plants are those that are easily damaged by frost. These plants include annuals, such as impatiens and marigolds, as well as some vegetables, such as tomatoes and peppers. Cold-sensitive plants should not be planted outdoors until after the last spring frost has occurred.
If cold-sensitive plants are exposed to frost, they can suffer from a variety of problems, including wilting, yellowing leaves, and stunted growth. In severe cases, frost can kill cold-sensitive plants.
To avoid damage from frost, gardeners should wait to plant cold-sensitive plants until after the last spring frost has occurred. Gardeners can also protect cold-sensitive plants from frost by covering them with a blanket or tarp on nights when frost is expected.
By following these tips, gardeners can protect their cold-sensitive plants from frost damage and ensure a successful growing season.
The general last spring frost dates given above are just estimates. The actual date of the last frost can vary depending on a number of factors, including location, elevation, and weather conditions. Therefore, it is important to check the local frost dates for your specific area.
The last spring frost date can vary depending on your location. For example, areas that are located near large bodies of water or in valleys tend to have later frost dates than areas that are located inland or at higher elevations.
The last spring frost date can also vary depending on your elevation. Areas that are located at higher elevations tend to have later frost dates than areas that are located at lower elevations.
The last spring frost date can also vary depending on the weather conditions. For example, a late-season cold snap can push back the last spring frost date. Similarly, a warm spring can advance the last spring frost date.
To find the local frost dates for your specific area, you can consult with your local Cooperative Extension office or visit the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) website.
If frost is expected, there are a number of things that gardeners can do to protect their plants. One option is to use covers. Covers can be made from a variety of materials, such as plastic, fabric, or burlap. Covers work by trapping heat and protecting plants from the cold air.
Another option is to use mulch. Mulch is a layer of material, such as straw, hay, or leaves, that is spread around plants. Mulch works by insulating the soil and protecting plants from the cold air.
When using covers or mulch to protect plants from frost, it is important to make sure that the plants are completely covered. It is also important to remove the covers or mulch as soon as the danger of frost has passed.
By following these tips, gardeners can protect their plants from frost damage and ensure a successful growing season.
One of the best ways to protect plants from frost damage is to monitor the weather forecast and be prepared to take action if a frost is predicted. Most weather forecasts will include a frost warning if there is a risk of frost in the coming days.
The weather forecast can change quickly, so it is important to check it regularly, especially during the spring and fall months when frost is most likely to occur.
Most weather forecasts will use a color-coded system to indicate the risk of frost. A green warning means that there is no risk of frost, a yellow warning means that there is a low risk of frost, and a red warning means that there is a high risk of frost.
If a frost warning is issued, there are a number of things that gardeners can do to protect their plants, such as covering them with a blanket or tarp, or using a space heater to raise the temperature around the plants.
If a frost warning is issued, it is important to take action as soon as possible. Waiting until the last minute can increase the risk of frost damage to plants.
For many gardeners, starting seeds indoors is a great way to get a jump on the growing season. By starting seeds indoors, gardeners can protect their seedlings from the cold weather and extend the growing season. However, it is important to start seeds indoors at the right time. If seeds are started too early, they may become leggy and weak. If seeds are started too late, the seedlings may not have enough time to mature before the last frost.
A good rule of thumb is to start seeds indoors 6-8 weeks before the last spring frost date. This will give the seedlings enough time to grow strong and healthy before they are transplanted outdoors.
1. Fill your seed starting trays or pots with seed starting mix.
2. Moisten the seed starting mix.
3. Sow the seeds according to the directions on the seed packet.
4. Cover the seeds with a thin layer of seed starting mix.
5. Water the seeds lightly.
6. Place the seed starting trays or pots in a warm place.
7. Keep the seed starting mix moist.
8. Once the seedlings have emerged, provide them with plenty of light.
By following these steps, you can successfully start seeds indoors and get a jump on the growing season.
Hardening off seedlings is the process of gradually exposing them to outdoor conditions before transplanting them into the garden. This helps the seedlings to adapt to the colder temperatures and the stronger sunlight. Hardening off seedlings also helps to reduce the risk of transplant shock.
To harden off seedlings, start by placing them outdoors for a few hours each day in a shaded area. Gradually increase the amount of time that the seedlings spend outdoors each day, and move them to a sunnier location. By the end of the hardening off period, the seedlings should be able to tolerate full sun and outdoor temperatures.
By following these tips, you can successfully harden off your seedlings and prepare them for transplanting into the garden.
Overwatering is one of the most common mistakes that gardeners make. Overwatering can lead to a number of problems, including root rot, which is a fungal disease that can kill plants. Root rot occurs when the roots of a plant are constantly wet, which prevents them from absorbing oxygen. This can lead to the plant wilting, yellowing, and eventually dying.
To avoid overwatering, it is important to water plants only when they need it. The best way to tell if a plant needs water is to feel the soil. If the soil is dry to the touch, it is time to water the plant. It is also important to water plants slowly and deeply, so that the water has time to soak into the soil and reach the roots.
Question 1: When is the last spring frost in 2025?
Answer 1: The last spring frost in 2025 is expected to occur on May 15th in the northern United States and April 15th in the southern United States.
Question 2: What should I plant after the last spring frost?
Answer 2: After the last spring frost, you can plant warm-season crops, such as tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, squash, and melons.
Question 3: What should I do if I have cold-sensitive plants?
Answer 3: Cold-sensitive plants should not be planted outdoors until after the last spring frost. If you have cold-sensitive plants, you can start them indoors 6-8 weeks before the last frost and then transplant them outdoors after the danger of frost has passed.
Question 4: How can I protect my plants from frost?
Answer 4: You can protect your plants from frost by using covers or mulch. Covers can be made from a variety of materials, such as plastic, fabric, or burlap. Mulch is a layer of material, such as straw, hay, or leaves, that is spread around plants.
Question 5: What should I do if a frost warning is issued?
Answer 5: If a frost warning is issued, you should take action to protect your plants from frost damage. You can do this by covering them with a blanket or tarp, or using a space heater to raise the temperature around the plants.
Question 6: How can I harden off my seedlings?
Answer 6: Hardening off seedlings is the process of gradually exposing them to outdoor conditions before transplanting them into the garden. This helps the seedlings to adapt to the colder temperatures and the stronger sunlight. To harden off seedlings, start by placing them outdoors for a few hours each day in a shaded area. Gradually increase the amount of time that the seedlings spend outdoors each day, and move them to a sunnier location. By the end of the hardening off period, the seedlings should be able to tolerate full sun and outdoor temperatures.
Closing Paragraph for FAQ
These are just a few of the frequently asked questions about the last spring frost in 2025. For more information, please consult with your local Cooperative Extension office or visit the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) website.
In addition to the information provided in the FAQ, here are a few additional tips for dealing with the last spring frost:
Tip 1: Check your local frost dates.
The general last spring frost dates given above are just estimates. The actual date of the last spring frost can vary depending on a number of factors, including location, elevation, and weather conditions. Therefore, it is important to check the local frost dates for your specific area.
Tip 2: Protect your plants from frost.
If frost is expected, there are a number of things that you can do to protect your plants, such as using covers or mulch. Covers can be made from a variety of materials, such as plastic, fabric, or burlap. Mulch is a layer of material, such as straw, hay, or leaves, that is spread around plants.
Tip 3: Harden off your seedlings.
Hardening off seedlings is the process of gradually exposing them to outdoor conditions before transplanting them into the garden. This helps the seedlings to adapt to the colder temperatures and the stronger sunlight. To harden off seedlings, start by placing them outdoors for a few hours each day in a shaded area. Gradually increase the amount of time that the seedlings spend outdoors each day, and move them to a sunnier location. By the end of the hardening off period, the seedlings should be able to tolerate full sun and outdoor temperatures.
Tip 4: Avoid overwatering.
Overwatering is one of the most common mistakes that gardeners make. Overwatering can lead to a number of problems, including root rot, which is a fungal disease that can kill plants. To avoid overwatering, it is important to water plants only when they need it. The best way to tell if a plant needs water is to feel the soil. If the soil is dry to the touch, it is time to water the plant.
Closing Paragraph for Tips
By following these tips, you can help your plants survive the last spring frost and thrive in the growing season ahead.
The last spring frost can be a challenging time for gardeners, but by following the tips provided in this article, you can protect your plants and ensure a successful growing season.
The last spring frost is a significant event for gardeners, as it marks the end of the cold weather and the beginning of the growing season. The date of the last spring frost can vary from year to year, depending on the weather conditions. In 2025, the last spring frost is expected to occur on May 15th in the northern United States and April 15th in the southern United States.
Gardeners should be aware of the last spring frost dates for their specific area and should take steps to protect their plants from frost damage. This can be done by using covers or mulch, hardening off seedlings, and avoiding overwatering.
By following these tips, gardeners can help their plants survive the last spring frost and thrive in the growing season ahead.
The last spring frost is a reminder that winter is coming to an end and that spring is on its way. With a little planning and preparation, gardeners can protect their plants from frost damage and ensure a successful growing season.